
一 多线程同步
由于CPython的python解释器在单线程模式下执行,所以导致python的多线程在很多的时候并不能很好地发挥多核cpu的资源。大部分情况都推荐使用多进程。
python的多线程的同步与其他语言基本相同,主要包含:
Lock & RLock :用来确保多线程多共享资源的访问。
Semaphore : 用来确保一定资源多线程访问时的上限,例如资源池。
Event : 是最简单的线程间通信的方式,一个线程可以发送信号,其他的线程接收到信号后执行操作。
二 实例
1)Lock & RLock
Lock对象的状态可以为locked和unlocked,
使用acquire()设置为locked状态; 使用release()设置为unlocked状态。如果当前的状态为unlocked,则acquire()会将状态改为locked然后立即返回。当状态为locked的时候,acquire()将被阻塞直到另一个线程中调用release()来将状态改为unlocked,然后acquire()才可以再次将状态置为locked。
Lock.acquire(blocking=True, timeout=-1),blocking参数表示是否阻塞当前线程等待,timeout表示阻塞时的等待时间 。如果成功地获得lock,则acquire()函数返回True,否则返回False,timeout超时时如果还没有获得lock仍然返回False。
实例:(确保只有一个线程可以访问共享资源)
import threadingimport time num = 0lock = threading.Lock() def func(st): global num print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' try to acquire the lock') if lock.acquire(): print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' acquire the lock.' ) print (threading.currentThread().getName() +" :%s" % str(num) ) num += 1 time.sleep(st) print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' release the lock.' ) lock.release() t1 = threading.Thread(target=func, args=(8,))t2 = threading.Thread(target=func, args=(4,))t3 = threading.Thread(target=func, args=(2,))t1.start()t2.start()t3.start()
结果:
 RLock与Lock的区别是:RLock中除了状态locked和unlocked外还记录了当前lock的owner和递归层数,使得RLock可以被同一个线程多次acquire()。
RLock与Lock的区别是:RLock中除了状态locked和unlocked外还记录了当前lock的owner和递归层数,使得RLock可以被同一个线程多次acquire()。 2)Semaphore
Semaphore管理一个内置的计数器,
每当调用acquire()时内置计数器-1;
调用release() 时内置计数器+1;
计数器不能小于0;当计数器为0时,acquire()将阻塞线程直到其他线程调用release()。
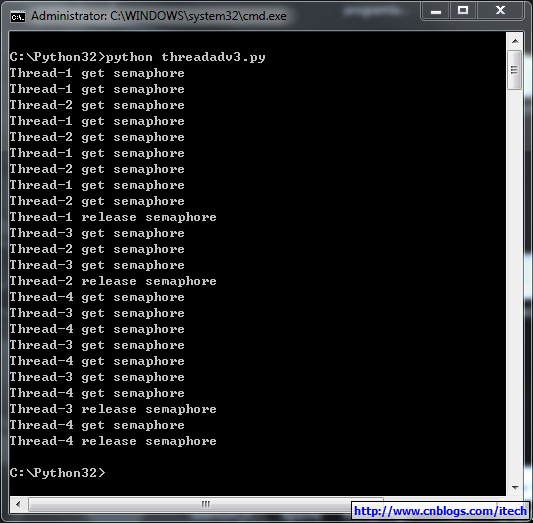
实例:(同时只有2个线程可以获得semaphore,即可以限制最大连接数为2):
import threadingimport time semaphore = threading.Semaphore(2) def func(): if semaphore.acquire(): for i in range(5): print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' get semaphore') semaphore.release() print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' release semaphore') for i in range(4): t1 = threading.Thread(target=func) t1.start()
结果:
3) Event
Event内部包含了一个标志位,初始的时候为false。
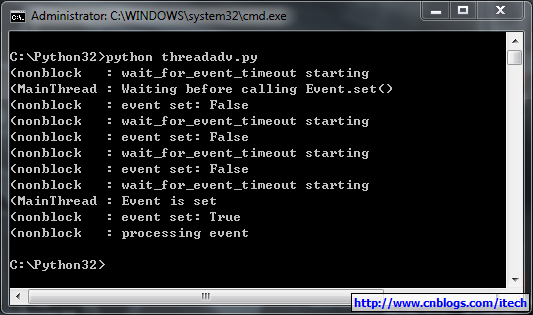
可以使用使用set()来将其设置为true; 或者使用clear()将其从新设置为false; 可以使用is_set()来检查标志位的状态; 另一个最重要的函数就是wait(timeout=None),用来阻塞当前线程,直到event的内部标志位被设置为true或者timeout超时。如果内部标志位为true则wait()函数理解返回。实例: (线程间相互通信)
import loggingimport threadingimport timelogging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,format="(%(threadName)-10s : %(message)s",)def wait_for_event_timeout(e, t): """Wait t seconds and then timeout""" while not e.isSet(): logging.debug("wait_for_event_timeout starting") event_is_set = e.wait(t) logging.debug("event set: %s" % event_is_set) if event_is_set: logging.debug("processing event") else: logging.debug("doing other work") e = threading.Event()t2 = threading.Thread(name="nonblock",target=wait_for_event_timeout,args=(e, 2))t2.start()logging.debug("Waiting before calling Event.set()")time.sleep(7)e.set()logging.debug("Event is set") 运行结果:
三 其他
1) 线程局部变量
线程局部变量的值是跟线程相关的,区别与全局的变量。使用非常简单如下:
mydata = threading.local()
mydata.x = 1
2)对Lock,semaphore,condition等使用with关键字代替手动调用acquire()和release()。
完!